These lessons, with videos, examples and step-by-step solutions, explain how to solve time-distance-rate problems.
Share this page to Google ClassroomDistance problems are word problems that involve the distance an object will travel at a certain average rate for a given period of time.
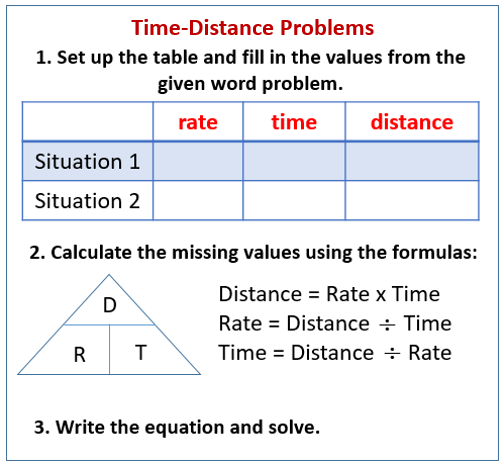
The formula for distance problems is: distance = rate × time or d = r × t.
Things to watch out for:
Make sure that you change the units when necessary. For example, if the rate is given in miles per hour and the time is given in minutes then change the units appropriately.
It would be helpful to use a table to organize the information for distance problems. A table helps you to think about one number at a time instead being confused by the question.
The following diagram shows how to set up a table to help solve time-distance problems. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions on how to solve distance problems.

Example:
John took a drive to town at an average rate of 40 mph. In the evening, he drove back at 30 mph. If he spent a total of 7 hours traveling, what is the distance traveled by John?
Solution:
Step 1: Set up a rtd table.
Step 2: Fill in the table with information given in the question.
John took a drive to town at an average rate of 40 mph. In the evening, he drove back at 30 mph. If he spent a total of 7 hours traveling, what is the distance traveled by John?
Let t = time to travel to town.
7 – t = time to return from town.